Understanding Form Controls Event.
I hope you enjoyed last week’s article and the little demo on user-defined custom events in a Form’s Class Module. We looked at how events can be defined and raised in one form, and then captured in another form’s Class Module to run the related event procedure. You might have a few questions about how this works, and I’m excited to dig a bit deeper with you in the coming weeks to make the whole idea even clearer.
When we design an Access form, we usually add controls like TextBoxes, Command Buttons, or ComboBoxes. Each of these comes with its own built-in events and actions that fire when triggered. Those events are then handled by their Event Procedures, where we write VBA code to carry out the task we want.
In the past, we would keep adding objects to a form, rely on their built-in events, and write VBA code to handle whatever needed to be done—often without really knowing how those events actually worked. Over time, this way of coding just became second nature: add a control, hook into its event, and move on. Recently, though, I wanted to dig a little deeper. From a practical standpoint, I started exploring the inner workings of these processes to better understand what’s really happening behind the scenes.
When talking about events on a form, three keywords are especially important to remember: Event, RaiseEvent, and WithEvents. You use Event to define a new event, RaiseEvent to trigger or fire it, and WithEvents to capture it in an event procedure. These three work together as the foundation of how custom events are created, raised, and handled—and you’ll see them in action in the examples below and in upcoming articles.
- Defines an event in the Form1 Class Module using the keyword Event: Public Event QtyUpdate(). This is the conventional method for defining Access events.
Fire the Event with the Keyword RaiseEvent: RaiseEvent QtyUpdate() in the Form1 Class Module.
To capture the event in the Form2 class module, we first need to create an instance of the Form1 class module using the declaration:
One key point to remember: a user-defined event can’t be captured within the same form where it’s defined. That’s because the event only becomes “catchable” when the form is instantiated as an object using the WithEvents keyword. In other words, the fired event on Form1 can only be handled by another form (like Form2) that’s set up to listen for it.
The resultant Event Procedure of 'ofrm_QtyUpdate()' Event must be written in the target Form Module. The ofrm_ prefix to the Subroutine name is taken from the Event Capturing declaration: Private WithEvents ofrm As Form_Form1.
Private Sub ofrm_QtyUpdate() 'VBA Code End Sub
User-Defined Event Example-2.
To enhance comprehension of the mentioned keywords, let’s explore a new example involving user-defined events. Imagine we have a textbox, enabling users to input a quantity with specific constraints. Our objective is to transmit the entered value to another form through a user-defined event for validation, and subsequently receive a relevant validation message in response.
To achieve this goal, we can define a Public Event named QtyUpdate() using the Event keyword. Subsequently, we can raise this event using the RaiseEvent keyword, passing the entered value as an argument. The event can then be captured in the class module of another open form using WithEvents, where the parameter value can be validated within an event procedure. Based on the validity of the parameter value, a suitable message can be displayed to the user.
To implement this action, let’s create two straightforward forms. In essence, we’ll define the events in the first form and execute the corresponding user-defined event procedure code in the second form’s class module.
The Event will be defined and fired from the first Form. The Raised Event action in the first form is captured in the second Form's Class Module and executes the Event Subroutine Code there.
With this foundational understanding, our intention is to restructure the code typically written within the Form Module into separate Class Modules, thereby allowing the Form to focus solely on user-interface design. This strategic approach is anticipated to significantly streamline project development timelines.
Let us try something very simple to understand the concept a little more.
Open your Database
Create a new Form
Insert a Textbox
Display the Property Sheet of the Textbox.
-
Change the Name Property value: OrderQty (Qty stands for Quantity).
-
Change the child Label Caption value: Quantity (1 - 5 only).
-
Insert a Command Button below the Textbox and change its Name Property value to cmdClose.
Change its Caption property to 'Close Form'.
-
Add another Command Button below the earlier one and change its Name Property Value to cmdOpen.
Change the Caption Property value to 'Open Event Capture Form'
Display the Form's Property Sheet. Set the Record Selectors Property Value No.
Set Navigation Buttons to No.
Set Scroll Bars to Neither.
Right-click on the TextBox and select Properties from the displayed Menu.
Select the AfterUpdate [Event Procedure] option on the TextBox Property and click on the Build (...) Button to open the VBA Module.
-
Copy and paste the following VBA Code into the Form's Module, overwriting existing lines, if any:
Option Compare Database Option Explicit 'User-Defined Events 'will Capture in Second Form Module. Public Event QtyUpdate(mqty As Single) Public Event formClose(txt As String) Private Sub cmdOpen_Click() DoCmd.OpenForm "frmUDCapture", acNormal End Sub Private Sub OrderQty_AfterUpdate() 'Announce the Event and pass the OrderQty as Prameter RaiseEvent QtyUpdate(Me!OrderQty) End Sub Private Sub cmdClose_Click() 'Announce the Event and pass the Text as Parameter RaiseEvent formClose("Close the Form?") End Sub Private Sub Form_Unload(Cancel As Integer) DoCmd.Close acForm, "frmUDCapture" End Sub -
Save the Form with the Name frmUserDefined.
User-Defined Events.
In the global declaration area of the form's class module, we have defined two user-defined events that closely resemble functions.
Public Event QtyUpdate(mqty As Single) Public Event formClose(txt As String)
Access has built-in events that also look like functions, such as Text0_Exit(Cancel As Integer), Form_Unload(Cancel As Integer), and Form_MouseMove(Button As Integer, Shift As Integer, X As Single, Y As Single).
The user-defined event declarations both begin with the keywords Public Event, followed by the event name and any associated parameters enclosed in parentheses. It is important to note that the event name should not contain an underscore character (e.g., Public Event Qty_Update()). Additionally, the declaration must have a Public scope.
The first user-defined event is designed to validate the contents of the OrderQty textbox whenever it is updated on the form. The second event (RaiseEvent formClose()) is triggered by the first command button click to close the form and passes a text message as a parameter.
After entering a numeric value into the OrderQty TextBox and pressing the enter key, the OrderQty_AfterUpdate event procedure of the textbox is executed as usual. Within this event procedure, the RaiseEvent QtyUpdate(Me!OrderQty) statement is executed, which triggers the first user-defined event and passes the OrderQty textbox value as the parameter.
Private Sub OrderQty_AfterUpdate() 'RaiseEvent and pass the OrderQty as a parameter RaiseEvent QtyUpdate(Me!OrderQty) End Sub
In Access, we typically write event procedures for objects, like TextBoxes and Command Buttons, directly in the same form module. These objects are part of Access itself and have their own built-in event triggering mechanisms that can be captured in the Form Module. That’s why their event procedures live right inside the form’s class module.
Later, we’ll take a closer look at how this built-in process works—and why it’s different from the way we handle user-defined events. You might already be wondering about those differences, and we’ll dive into them shortly.
When you declare a Form1 object instance with the WithEvents keyword in the Form2 module (Public WithEvents ofrm As Form_Form1)Any events defined and raised in the Form1 module can be captured by event procedures written in the Form2 module. The same principle applies if the events come from a standalone class module instead of Form1. This works because the WithEvents keyword essentially “listens” for events raised by the class object and allows the form or class module to respond by executing the corresponding event procedures.
The User-defined events are not related to any object-based events, like the built-in events of a TextBox. The only mechanism for raising a user-defined event is to explicitly call the RaiseEvent statement in the code, as we did in the example.
Additionally, a user-defined event declaration doesn't have any inherent mechanism of its own, like a TextBox. It simply defines the event's name, any parameters it may have, and its public accessibility. It's up to the programmer to implement the code that raises the event and the code that handles the event when it's raised.
It's also worth noting that a user-defined event can be raised only from the Class Module of a Form or from a stand-alone Class Module. However, as I mentioned earlier, to capture the event in another module, that module must use the WithEvents keyword to declare an Instance of the Class Module of the first Form.
The RaiseEvent statement within the OrderQty_AfterUpdate() event procedure announces the QtyUpdate() user-defined event and passes the OrderQty value as a parameter. This QtyUpdate() event is then captured in the second form's module, the Event Procedure is executed, and it validates the OrderQty value.
The cmdClose_Click() event procedure in the frmUserDefined Form raises the formClose() event with a message text as the parameter. Then, the second Form's Module captures this event and shows the message text to the User to determine whether to close the frmUserDefined Form or not, based on the User's responses.
This is a simple example of how user-defined events can be used to communicate between different Forms or Class Modules in VBA.
Private Sub cmdClose_Click()
'Announce the Event and pass the Text as Parameter
RaiseEvent formClose("Close the Form?")
End Sub
Private Sub Form_Unload(Cancel As Integer)
DoCmd.Close acForm, "frmUDCapture"
End Sub
The Form_Unload() event of the frmUserDefined form is triggered first, as the form is closed, and the frmUDCapture Form is closed first.
The Form_Close() event is triggered next after the frmUDCapture form is closed and closes the frmUserDefined Form in the cmdClose_Click() event procedure.
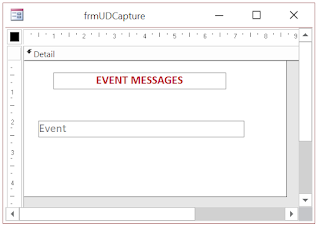
The User-Defined Event Capturing Form.
Create a new Form and open it in Design View.
Insert two labels as shown in the Image of the Form's design view given below.
Change the first label caption to EVENT MESSAGES.
Select the second label and display its Property Sheet.
Change the Name Property Value to Label2, if it is different.
Change the Caption Property Value to Event.
Display the Form's Property Sheet. Set the Record Selectors Property Value: No.
Set Navigation Buttons to No.
Set Scroll Bars to Neither.
Change the Detail Section Area of the Form to as small as shown in the above Image.
Display the Form's VBA Module.
Copy the following VBA Code and paste it over the existing lines, if any, in the Module.
Option Compare Database Option Explicit Public WithEvents ofrm As Form_frmUserDefined Private Sub Form_Load() On Error Resume Next
Set ofrm = Forms("frmUserDefined")
End Sub Private Sub ofrm_QtyUpdate(sQty As Single) Dim Msg As String If Nz(sQty, 0) < 1 Or Nz(sQty, 0) > 5 Then Msg = "Valid Qty Range: 1 - 5 Only" Else Msg = "Order Qty: " & sQty & " Approved." End If Me.Label2.Caption = Msg MsgBox Msg, vbInformation, "QtyUpdate()" End Sub Private Sub ofrm_formClose(txt As String) Me.Label2.Caption = txt If MsgBox(txt, vbYesNo, "FormClose()") = vbYes Then DoCmd.Close acForm, ofrm.Name Else Me.Label2.Caption = "Close Action = Cancelled." End If End SubSave the Form with the Name frmUDCapture and Close it.
Event Capturing Form Module VBA Code Review.
Public WithEvents ofrm As Form_frmUserDefined
Private Sub Form_Load()
On Error Resume Next
Set ofrm = Forms("frmUserDefined")
End Sub
The line of code Public WithEvents ofrm As Form_frmUserDefined is a crucial global declaration in the second Form's Class Module. It declares a new instance of the first Form, frmUserDefined, as an Event Listener Object variable named ofrm.
This is important because it enables the second Form Module to capture and respond to events that are raised by the first Form. By the above declaration, the Listener Object in the second Form can intercept and handle user-defined events raised by the frmUserDefined.
Without this declaration, the second Form would be unable to capture and respond to events raised by the first Form, and the user-defined event functionality would not work as intended.
To make a long story short, we are declaring an Instance of the frmUserDefined Form's Class Module Object Variable name ofrm. The Form_ prefix to the Form Name indicates that we are referring to the Form's Class Module and will create an Instance of the Class Module.
The first Form's Class Module Object Instance will be assigned to the declared ofrm Object Variable through the frmUDCapture Form's Form_Load() Event Procedure.
The WithEvents keyword declares the ofrm as a Listener Object to capture the Events Raised from its original Class Module-based user-defined Events.
Note: Remember, the WithEvents classification can be made only when an instance of any Object, like Form, TextBox, ComboBox, etc., is created.
The general rule of Object Instance creation as a Listener Property is that:
The WithEvents keyword is used in the parent Class Module to create a connection between the object and its events. This connection allows the Class Module to capture events fired by the object and call the corresponding event procedure in response.
The Event Subroutine name must start with the object instance name, followed by an underscore, and then the event name. This naming convention ensures that Access can properly map the event to the correct event procedure.
For example, if we have a TextBox object Instance named "txtName" and we want to capture its LostFocus event, we would declare it in the parent Class Module like this:
Private WithEvents txtName As Access.TextBox Private Sub txtName_LostFocus() ' Do something when the txtName TextBox loses focus End SubIn this example, the object instance name "txtName" is prefixed to the event name "LostFocus" to create the event procedure name "txtName_LostFocus".
To capture the user-defined event QtyUpdate() from the frmUserDefined form module, the parent form module instance should be declared with the WithEvents keyword. This allows the frmUDCapture form to listen to the event transmission from the frmUserDefined form and execute the corresponding event procedure.
Note: When you add a TextBox (or any other Access Object) to a form in Access, the Access system creates an instance of the TextBox object and adds it as a control to the form. The Name property will be filled with a default name followed by the text "As TextBox" appended to it. For example, if the default name of the TextBox is "Text0", then the TextBox Control's Property declaration on the Form will be:
Private WithEvents Text0 As TextBox
You can change the name Text0 of the TextBox control to something more meaningful, like Quantity, and the name of the property declaration in the form's module will automatically update to reflect the name change. This declaration is not directly visible to us except for the Name Property Value. But it can be displayed through the Object Browser.
Check the last two lines at the bottom of the Object Browser image below and see how the TextBox Object Instance name OrderQty declaration appears on our Form frmUserDefined. Check the declaration starting with the Keyword WithEvents OrderQty As TextBox.
To inspect the Property of the TextBox in the Object Browser or any other control on the Form, you can follow these steps:
Right-click on the VBA Editing Window and select Object Browser Option, or click on the Object Browser Button from the Toolbar above to Open the Object Browser.
In the Object Browser, select the Database Name in the <All Libraries> Control.
The Object Browser will display the Properties and Methods of the selected control, including the declaration for the control's Object Instance.
Select the Form Name Form_frmUserDefined from the left panel of the Browser Window.
The Form's Property List appears in alphabetical order in the right-side Panel.
Scroll down and find the OrderQty Property of the TextBox and select it.
For example, the declaration for a TextBox with the name OrderQty on a form named frmUserDefined would look like this:
WithEvents OrderQty As TextBox
At the bottom panel of the Object Browser in the detail view of the selected Property.
Explore the user-defined Event QtyUpdate() declaration and how it appears in the right panel with a lightning icon, and check the details view of the event declaration in the bottom panel.
Both user-defined events and built-in events of Access objects require an event procedure to be created on their parent VBA module. For built-in events, the event procedure name will be based on the name of the Access object and the event name. For example, if the Access object is a Textbox named "Text0" and the Event is "LostFocus", the event procedure name will be "Sub Text0_LostFocus()".
The User-defined Event Subroutine name consists of two parts. The first part is the Event Subroutine name Prefix, and the second part is the Event Name. The first part is the First Form Module's Instance name declared with the WithEvents keyword in the second Form Module - objFrm. The second part is the QtyUpdate, like objFrm_QtyUpdate(); both parts are separated by an underscore character.
The LostFocus event is an inbuilt event of the TextBox control in Access. When you add a TextBox control to a form, Access creates an instance of the TextBox object and assigns it a default name such as Text0. This TextBox instance is then declared as a property of the form, with the WithEvents keyword, which allows it to capture and handle its inherent events.
As I mentioned, the Text0 object's parent object is the class module of the form, which means that the event handling code in the LostFocus event (or any other inbuilt event) should be written in the form's class module. The naming convention for event procedures for controls is that they start with the name of the control instance, followed by an underscore, and then the name of the event. In the case of the TextBox control named Text0, the event procedure for the LostFocus event would be named Sub Text0_LostFocus().
Several Textbox object instances can be created in the same Form with appropriate names, and their Event Subroutines are written in the same Form's Class Module with TextBox names as the prefix. This is what we normally do on the Form Module.
The QtyUpdate() event is a user-defined event and is not part of any built-in object, like the LostFocus event of a TextBox. It is defined in the Class Module of the frmUserDefined Form, and the parent object of the event is the form's Class Module.
In the frmUDCapture form, we have declared an instance of the frmUserDefined form as a listener parent object using the WithEvents keyword. Since the Form Class Module instance is named "ofrm", the event procedure for the QtyUpdate() event will have the format "Sub ofrm_QtyUpdate()". This allows the frmUDCapture form to capture and respond to the QtyUpdate() event raised by the frmUserDefined form.
The statement Set ofrm = Forms("frmUserDefined") statement within the Form_Load() Event Procedure of the frmUDCaptured Form Module, and if the Form is in an open state, then assigns it to the ofrm Class Module object. If this form is not in the open state, then it will run into an Error. The On Error Resume Next statement will suppress the error message, but the Event capturing will not work as expected.
Ensure that you open the frmUserDefined Form first, then the second form, frmUDCapture next.
We enter a Numeric Quantity Value into the OrderQty Textbox on the Form frmUserDefined and press the Enter Key to complete the data entry. The RaiseEvent QtyUpdate(Me!OrderQty) is fired from within the OrderQty_AfterUpdate() Event Procedure.
This Event is captured in the frmUDCapture Form's Event Procedure Subroutine Code given below:
Private Sub ofrm_QtyUpdate(sQty As Single) Dim Msg As String If Nz(sQty, 0) < 1 Or Nz(sQty, 0) > 5 Then Msg = "Valid Qty Range: 1 - 5 Only" Else Msg = "Order Qty: " & sQty & " Approved." End If Me.Label1.Caption = Msg MsgBox Msg, vbInformation, "QtyUpdate()" End SubThe Valid value Range accepted in the TextBox is 1 to 5 only. Normally, we write this validation check procedure in the same Form Module Event Subroutine only. Here, we are running the validity check in the second Form Module, and an appropriate message is saved into the Msg String Variable and displayed in the MsgBox too. It will update the same message text in the Label Control Caption Property on the second Form, to view the message after closing the Message Box.
Check the Event Subroutine line: Private Sub ofrm_QtyUpdate(sQty As Single)
The frmUserDefined Form's Class Module Object Instance name ofrm is used as the Subroutine name prefix, combined with the User-Defined Event name QtyUpdate(), both separated by an underscore character.
Similarly, the FormClose() Event is captured by the Private Sub 'ofrm_formClose (txt As String)' Event Procedure and displays the message that passed as a parameter to the User, whether to close the Form frmUserDefined (first form) now, or not. If the response is Yes, then it closes the First Form.
Private Sub ofrm_formClose(txt As String) Me.Label2.Caption = txt If MsgBox(txt, vbYesNo, "FormClose()") = vbYes Then DoCmd.Close acForm, ofrm.Name Else Me.Label2.Caption = "Close Action = Cancelled." End If End Sub
In the formClose() Event Procedure header line, you can see that the ofrm object prefix is appearing. In this subroutine, the parameter text is displayed in the message box, and the user responds whether the frmUserDefined Form (the first Form) should be closed or not. The Message text is displayed from the second Form's Event Procedure. If the response is Yes, then it runs the Code to close the first Form.
When we issue Docmd.OpenForm "FormName" Command a series of Events takes place in a certain order: Form Open, Form Load, Form Current in that sequence. Similarly, when we run the DoCmd.Close acForm, "FormName" Form_Unload Event runs first before the Form_Close event, if both events are run in VBA.
When the Form_Close() Event Procedure is called to close the first Form, the Form_Unload() event fires first (if this Event Code is present in the form Module), and closes the second form 'frmUDCapture' first, before closing the first form: frmUserDefined.
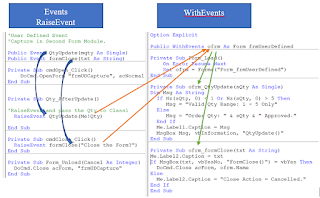
The User-Defined Events Trajectory View.
From the above graphical image, we can easily see at a glance how the user-defined Event is declared with the Event Keyword, how the Events are Announced with the RaiseEvent Keyword, and how the Event Listener declaration is done with the Keyword WithEvents that Captures the announced Event, identify it with the Event Procedure, and executes the correct Event Procedure Code.
Once we understand how Events and Event Procedures work behind the scenes, it becomes clear that an event procedure of a TextBox control on the form can actually be written in another form’s class module—something we already demonstrated in the example above. The same approach can also be applied using a form module together with one or more standalone class modules, giving us even more flexibility in how we structure our code.
But before touching the tricks at that level, we need to know a few basics of Event handling on Forms. How could we do things differently on Form, other than the traditional method we follow now?
Once we know how these tricks work together, our target is to take all the VBA codes out of the Form Module and organize them in such a way that Coding becomes very easy. We will use the Forms for User Interface design only.
Besides that, once we streamline the existing Form Module Coding procedure in a standalone Class Module, we can independently manage the Event Procedure VBA Coding, without opening the Form in Design View hundreds of times for coding and modifying. Besides that, the repetitive nature of Code (example: that highlights the background of TextBoxes when active) needs only one Event Procedure for all the text boxes, rather than repetition of the same Code for individual TextBoxes.
A Form with several types of Controls, like TextBoxes, Command Buttons, and frequently used other controls, and their various Event Procedures of several types are all mixed up and stored in the Form Module together. We will not be able to use any part of it for any other Project.
Download Demo Database
Streamlining Form Module Code in Standalone Class Module.
- Reusing Form Module VBA Code for New Projects.
- Streamlining Form Module Code - Part Two.
- Streamlining Form Module Code - Part Three
- Streamlining Form Module Code - Part Four
- Streamlining Form Module Code - Part Five
- Streamlining Form Module Code - Part Six
- Streamlining Form Module Code - Part Seven
- Streamlining Form Module Code - Part Eight
- Streamlining Form Module Code - Part Nine
- Streamlining Form Module Code - Part Ten
- Streamlining Form Module Code - Part Eleven
- Streamlining Report Module Code in Class Module
- Streamlining Module Code Report Line Hiding-13.
- Streamlining Form Module Code Part-14.
- Streamlining Custom Made Form Wizard-15.
- Streamlining VBA Custom Made Report Wizard-16.
- Streamlining VBA External Files List in Hyperlinks-17
- Streamlining Events VBA 3D Text Wizard-18
- Streamlining Events VBA RGB Color Wizard-19
- Streamlining Events Numbers to Words-20
- Access Users Group(Europe) Presentation-21
- The Event Firing Mechanism of MS Access-22
- One TextBox and Three Wrapper Class Instances-23
- Streamlining Code Synchronized Floating Popup Form-24
- Streamlining Code Compacting/Repair Database-25
- Streamlining Code Remainder Popup Form-26
- Streamlining Code Editing Data in Zoom-in Control-27
- Streamlining Code Filter By Character and Sort-28
- Table Query Records in Collection Object-29
- Class for All Data Entry Editing Forms-30
- Wrapper Class Module Creation Wizard-31
- wrapper-class-template-wizard-v2
















No comments:
Post a Comment
Comments subject to moderation before publishing.