Introduction.
Last week, we explored how to use the Dir() DOS command to read files from the disk one by one and display their names in the Debug window.
Building on that, we will now create a VBA utility that uses the Dir() command together with the very useful FileCopy statement (note that it is a statement, not a function) to read and transfer files from one folder to another location on the disk. The files can be of any type—for example, *.pdf, *.docx, *.xls, or *.* (all files).
This utility will read the files from a folder specified in a text box, list them in a list box using the Dir() command, and allow you to copy either all the listed files or only the selected ones to a target folder specified in another text box.
The Utility Form.
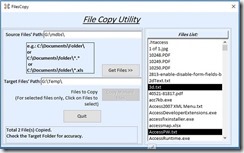
The design view image of a Form created for this purpose is given below for reference:
The form design is simple, consisting of two text boxes, one list box, three command buttons, and a label control to display messages from the utility program. You can download this utility form as part of a sample database at the end of this article.
These are the names of the Controls on the Form:
Top Text box: Source
Text Box 2: Target
List Box: List1
Top Command Button: cmdDir
Second Command Button: cmdSelected
Last Command Button: cmdClose
Bottom empty Label Name: msg
Note: If you are designing this form yourself, make sure that the same control names are used as described above. The VBA code you will copy into the module references these exact names.
In addition to the main controls, there is a Label control below the first (source) text box that provides examples of how to specify the source file path correctly.
Another label control at the bottom of the form displays messages during input validation and shows error notifications while the VBA code is executing.
An Image of a sample run of the FileCopy Statement is given below:
You can create this user interface using the control names provided above. Once the form is designed with the correct control names, open the VBA window for the form and copy the following code into its VBA module:
The Form Module Code.
Option Compare Database
Option Explicit
Dim strSource1 As String
Dim strSource2 As String, strMsg As String
Private Sub cmdClose_Click()
On Error GoTo cmdClose_Click_Error
If MsgBox("Close File Copy Utility?", vbOKCancel + vbQuestion, "cmdClose_Click()") = vbOK Then
DoCmd.Close acForm, Me.Name, acSaveYes
End If
cmdClose_Click_Exit:
Exit Sub
cmdClose_Click_Error:
MsgBox Err.Description, , "cmdClose_Click()"
Resume cmdClose_Click_Exit
End Sub
Private Sub cmdDir_Click()
'=========================================================
'Author : a.p.r.pillai
'Date : June 2018
'Purpose: Take directory listing
'Rights : All Rights Reserved by www.msaccesstips.com
'=========================================================
Dim strSource As String, strMsg As String
Dim i As Integer, x As String
Dim j As Integer, strfile As String
Dim strList As ListBox, LList As String
On Error GoTo cmdDir_Click_Err
msg.Caption = ""
'Read Source location address
strSource = Nz(Me!Source, "")
If Len(strSource) = 0 Then
strMsg = "Source Path is empty."
MsgBox strMsg,vbOKOnly + vbCritical, "cmdDir_Click()"
msg.Caption = strMsg
Exit Sub
End If
'check for the last back-slash location
'this can be used to split the folder name
'and file name type values separately.
i = InStrRev(strSource, "\")
'get the folder name part into the variable
strSource1 = Left(strSource, i)
'take file type (*.docx, *.exl, *.txt etc.) value into a separate
'variable temporarily
If Len(strSource) > i Then
strSource2 = Right(strSource, Len(strSource) - i)
End If
'define Listbox object
Set strList = Me.List1
'Read the first file from the folder
strfile = Dir(strSource, vbHidden)
If Len(strfile) = 0 Then
strMsg = "No Files of the specified type: '" & strSource2 & "' in this folder."
MsgBox strMsg, vbCritical + vbOKOnly, "cmdDir()"
msg.Caption = strMsg
Exit Sub
End If
j = 0
LList = ""
Do While Len(strfile) > 0
If Left(strfile, 1) = "~" Then 'ignore backup files, if any
GoTo readnext:
End If
j = j + 1 'File list count
LList = LList & Chr(34) & strfile & Chr(34) & ","
readnext:
strfile = Dir() ' read next file
Loop
LList = Left(LList, Len(LList) - 1) ' remove the extra comma at the end of the list
strList.RowSource = LList 'insert the files list into the listbox RowSource property
strList.Requery 'refresh the listbox
msg.Caption = "Total: " & j & " Files found."
Me.Target.Enabled = True
cmdDir_Click_Exit:
Exit Sub
cmdDir_Click_Err:
MsgBox Err.Description, , "cmdDir_Click()"
Resume cmdDir_Click_Exit
End Sub
Private Sub cmdSelected_Click()
'=========================================================
'Author : a.p.r.pillai
'Date : June 2018
'Purpose: Copy Selected/All Files to Target Location
'Rights : All Rights Reserved by www.msaccesstips.com
'=========================================================
Dim lstBox As ListBox, ListCount As Integer
Dim strfile As String, j As Integer, t As Double
Dim strTarget As String, strTarget2 As String
Dim chk As String, i As Integer, yn As Integer
Dim k As Integer
On Error GoTo cmdSelected_Click_Err
msg.Caption = ""
'Read Target location address
strTarget = Trim(Nz(Me!Target, ""))
'validate Destination location
If Len(strTarget) = 0 Then
strMsg = "Enter a Valid Path for Destination!"
MsgBox strMsg, vbOKOnly + vbCritical, "cmdSelected()"
msg.Caption = strMsg
Exit Sub
ElseIf Right(strTarget, 1) <> "\" Then
strMsg = "Correct the Path as '" & Trim(Me.Target) & "\' and Re-try"
MsgBox strMsg, vbOKOnly + vbCritical, "cmdSelected()"
msg.Caption = strMsg
Exit Sub
End If
'Take a count of files in listbox
Set lstBox = Me.List1
ListCount = lstBox.ListCount - 1
'take a count of selected files, if any, for copying
i = 0
For j = 0 To ListCount
If lstBox.Selected(j) Then
i = i + 1
End If
Next
'identify user's response for copy
If (i = 0) And (ListCount > 0) Then
strMsg = "Copy all Files..?"
Me.cmdSelected.Caption = "Copy All"
Else
strMsg = "Copy Selected Files..?"
Me.cmdSelected.Caption = "Copy Marked files"
End If
'Me.cmdSelected.Requery
'get copy option from User
yn = MsgBox(strMsg, vbOKCancel + vbQuestion, "cmdSelected_Click()")
'Run Copy selected option
If (i = 0) And (yn = vbOK) Then
GoSub allCopy
ElseIf (i > 0) And (yn = vbOK) Then
GoSub selectCopy
Else
Exit Sub
End If
'disable Copy button to stop a repeat copy of the same files.
'Remarks: User can make fresh selections from the same list
'To copy them to the same target locatiion.
'Or to a different location by specifying different Path
'in the Destination Text Box
Me.List1.SetFocus
Me.cmdSelected.Enabled = False
'Display copy status
strMsg = "Total " & k & " File(s) Copied." & vbCrLf & "Check the Target Folder for accuracy."
MsgBox strMsg, vbInformation + vbOKOnly, "cmdSelected_Click()"
Me.msg.Caption = strMsg
cmdSelected_Click_Exit:
Exit Sub
allCopy:
k = 0
For j = 0 To ListCount
strfile = lstBox.ItemData(j)
strSource2 = strSource1 & strfile
strTarget2 = strTarget & strfile
FileCopy strSource2, strTarget2
'give enough time to copy the file
'before taking the next file
k = k + 1
t = Timer()
Do While Timer() > (t + 10)
'do nothing
Loop
Next
Return
selectCopy:
k = 0
For j = 0 To ListCount
If lstBox.Selected(j) Then
strfile = lstBox.ItemData(j)
strSource2 = strSource1 & strfile
strTarget2 = strTarget & strfile
FileCopy strSource2, strTarget2
'give enough time to copy the file
'before taking the next file
k = k + 1
t = Timer()
Do While Timer() > (t + 10)
'do nothing
Loop
End If
Next
Return
cmdSelected_Click_Err:
MsgBox Err.Description, , "cmdSelected_Click()"
Me.msg.Caption = Err.Description
Resume cmdSelected_Click_Exit
End Sub
Private Sub List1_AfterUpdate()
On Error GoTo List1_AfterUpdate_Error
Me.cmdSelected.Enabled = True
List1_AfterUpdate_Exit:
Exit Sub
List1_AfterUpdate_Error:
MsgBox Err.Description, , "List1_AfterUpdate()"
Resume List1_AfterUpdate_Exit
End Sub
You may save the Form with the name FileCopy.
Note: FileCopy is a VBA Statement, not a built-in Function.
You can copy different sets of files from the list displayed in the list box to different target folders by first deselecting any previous selections, selecting the desired files, and updating the destination folder address in the text box.
Download the Demo Database.
You may download the sample database with the VBA Code from the Link given below: